Data Mesh vs Data Fabric
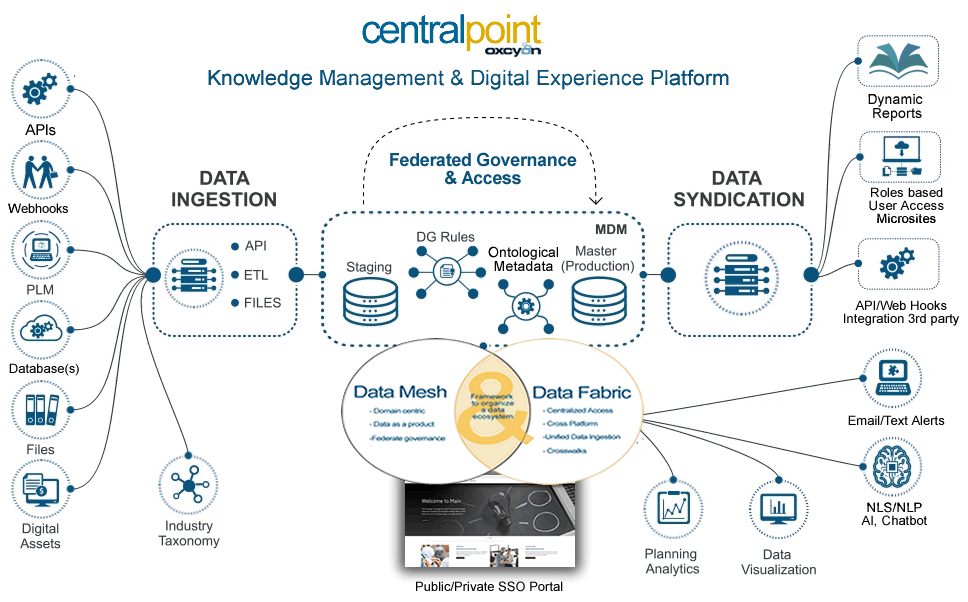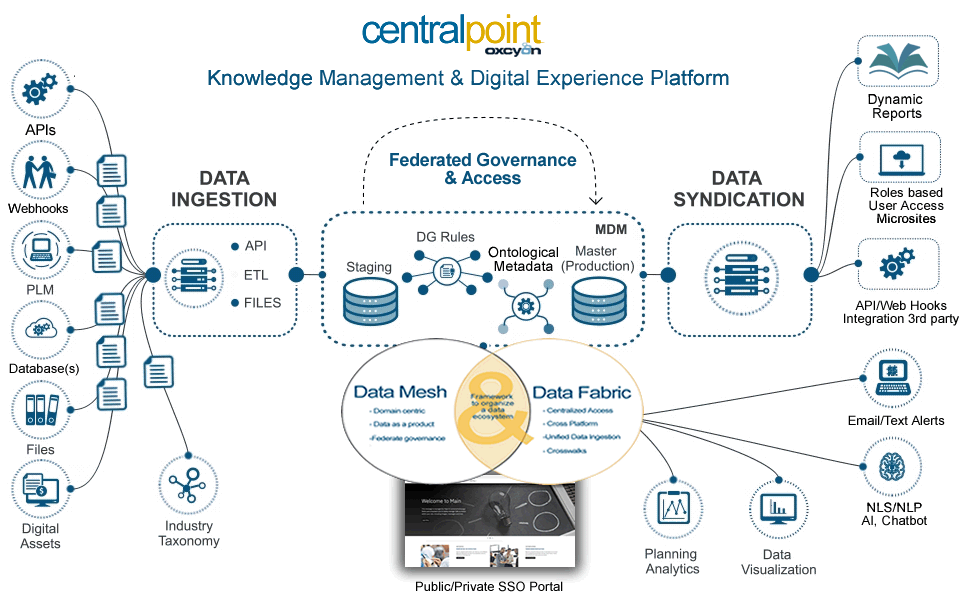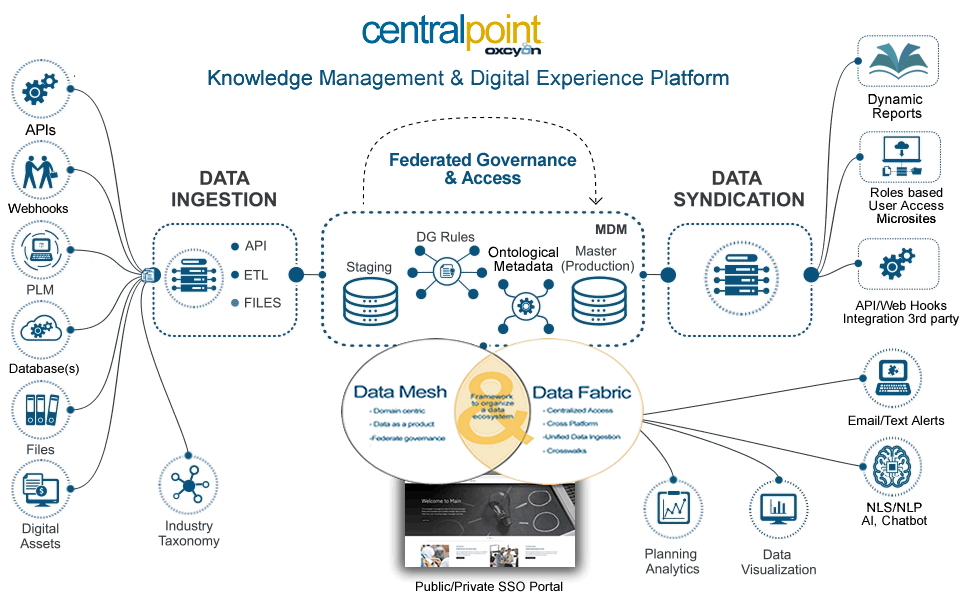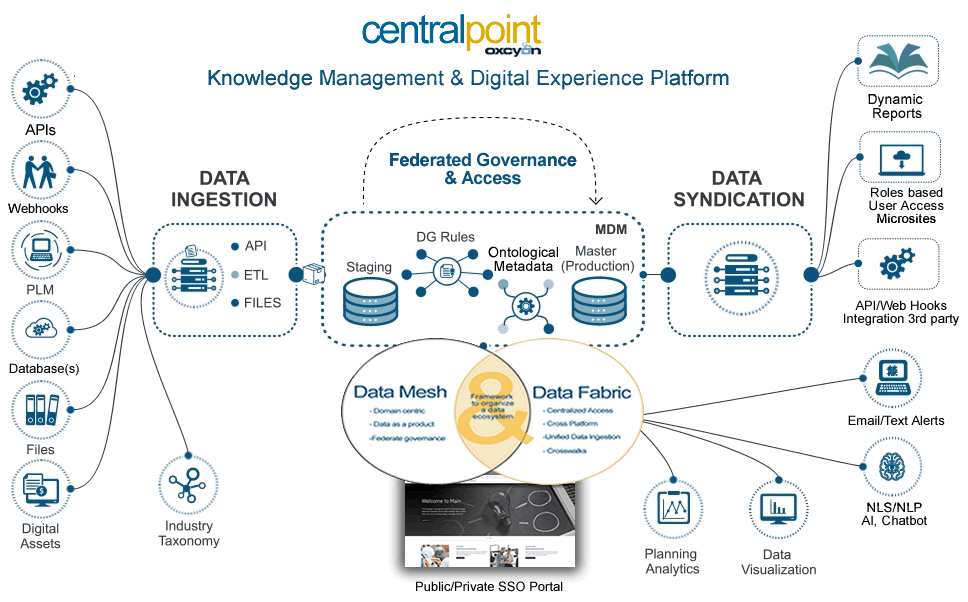
In the realm of modern data management, two concepts are gaining significant attention: data mesh and data fabric. Both aim to address the challenges of handling vast amounts of data across diverse sources, but they approach the problem from different angles. Understanding the distinction between these concepts is crucial for organizations looking to optimize their data strategies. Data mesh focuses on decentralizing data ownership and management, while data fabric emphasizes a unified architecture for seamless data integration and processing. Together, they enable comprehensive data management, including scanning, indexing, ingestion, and federated search, all while respecting user-specific rules and permissions.
 Data Mesh: Decentralized Data Ownership and Management
Data Mesh: Decentralized Data Ownership and Management
Data mesh is a relatively new concept that advocates for decentralized data management. It proposes shifting from a centralized data warehouse or lake approach to a distributed architecture where domain-specific teams manage their own data as products. This approach aims to overcome the limitations of traditional data architectures that often become bottlenecks due to centralized control and siloed data.
Key Characteristics of Data Mesh
1. Domain-Oriented Decentralization: Data ownership is distributed among domain-specific teams who have the best understanding of their data. Each team treats its data as a product, responsible for its quality, accessibility, and lifecycle.
2. Data as a Product: Each domain team is responsible for the full lifecycle of their data products, ensuring data quality, governance, and accessibility.
3. Self-Service Data Infrastructure: Data mesh promotes the use of self-service tools and platforms that enable domain teams to manage their data independently without relying on a central IT team.
4. Federated Computational Governance: Governance policies are applied consistently across the organization but are enforced in a decentralized manner, allowing for flexibility and local control.
Data Fabric: Unified Architecture for Seamless Data Integration
Data fabric, on the other hand, is a design concept that aims to create a unified data management framework. It provides a comprehensive architecture that integrates data from disparate sources, both structured and unstructured, and enables seamless data movement, transformation, and accessibility.
Key Characteristics of Data Fabric
1. Unified Data Integration: Data fabric connects diverse data sources across on-premise, cloud, and hybrid environments, providing a cohesive view of the data landscape.
2. Automated Data Management: It leverages automation and machine learning to manage data ingestion, transformation, and integration, ensuring data consistency and quality.
3. Scalability and Flexibility: Data fabric is designed to scale with the organization’s needs, accommodating growing data volumes and new data sources with ease.
4. Enhanced Data Accessibility: By providing a unified interface for accessing data, data fabric ensures that users can easily retrieve and utilize data from any source within the organization.
Complementary Roles: Data Mesh and Data Fabric in Practice
While data mesh and data fabric may seem like competing approaches, they are actually complementary and can be effectively combined to achieve robust data management. Data mesh brings the benefits of decentralized data ownership and domain-specific expertise, while data fabric provides the underlying infrastructure that ensures seamless data integration and accessibility.
Daily Scanning, Indexing, and Ingestion
- Data Mesh: Domain teams scan and index their own data products daily, ensuring that data is up-to-date and accurate. This decentralized approach allows for quicker response times and more relevant data management.
- Data Fabric: The data fabric framework ingests data from various sources, including the indexed data products from the data mesh, ensuring that all data is integrated and accessible through a unified interface. This ingestion process is automated and managed centrally, providing consistency and reliability.
Federated Search and User-Specific Rules
A key benefit of combining data mesh and data fabric is the ability to implement federated search, which respects user-specific rules and permissions.
- Federated Search: By indexing data through the mesh and ingesting it into the fabric, organizations can enable federated search capabilities that span all data sources. Users can perform searches across the entire data landscape while the system respects their login credentials and access permissions.
- User-Specific Rules: Both data mesh and data fabric ensure that data access is governed by user-specific rules. Data mesh allows domain teams to enforce access controls at the local level, while data fabric provides a central layer of security and governance that applies these rules consistently across all data sources.
Data mesh and data fabric represent two different but complementary approaches to modern data management. By combining decentralized data ownership with a unified integration framework, organizations can achieve the best of both worlds: localized expertise and control over data, along with seamless integration and accessibility. This synergy enables effective daily scanning, indexing, and ingestion of data, culminating in robust federated search capabilities that respect user-specific rules and permissions. Together, data mesh and data fabric empower organizations to unlock the full potential of their data.